|

Lab
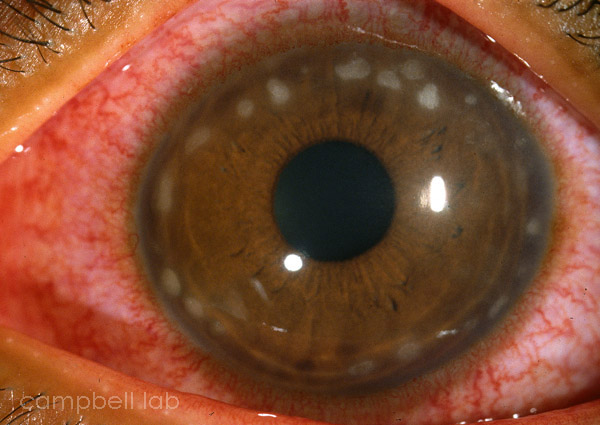
Diagnostic Testing: Chlamydia
Conjunctivitis due to Chlamydia can be an acute or chronic disease. Chlamydia trachomatis is an intracellular parasite which is currently tested using Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing (NAAT) (Gen-Probe® Aptima®).
Specimen Collection
PCR or NAAT
Specimen Collection
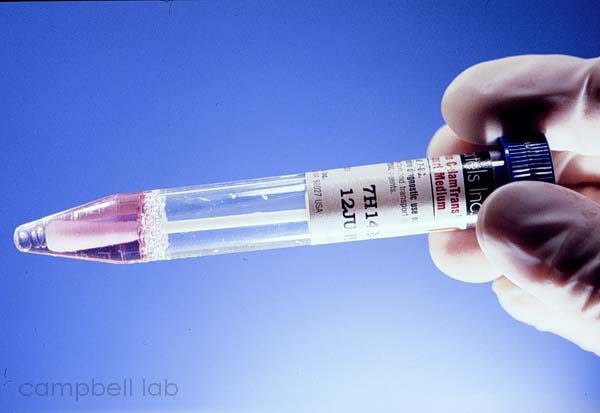
Specimens are directly collected by vigorously swiping the exposed conjunctiva with a plastic soft-tipped applicator. Cornea samples are not necessary. Topical anesthetic can be applied to the conjunctiva but this is optional. Samples are collected and are submitted using an Aptima swab. DO NOT USE VIRAL TRANSPORT MEDIUM THAT MAY CONTAIN ANTIBIOTICS THAT INHIBITS CHLAMYDIA GROWTH IN CELL CULTURE.
Aptima swab and transport media
(Click on image to enlarge)
 |
PCR or NAAT
We highly recommend PCR or NAAT testing for the detection of chlamydial DNA from ocular specimens. The problems are less with transportation of these specimens because live organisms are not necessary. Still, samples should be refrigerated and transported to the laboratory as soon as possible to avoid any possible enzymes that may degrade any DNA or rRNA. We advise ophthalmologists to make the effort to locate PCR or NAAT testing.

|